Founded in 2014, NIO has taken only a few years to gain a firm foothold in China’s premium auto market. A new research report attempts to find the answer.
In the report released earlier this week, Tianfeng Securities analyst Yu Te argues that NIO has a leading edge in electric technology, manufacturing, and business model, and that future growth is expected.
With the launch of new models, the easing of battery and chip shortages, and the gradual release of factory capacity, NIO’s sales and cash flow are expected to continue to improve, and its market capitalization has big growth potential, the analyst said.
Here are the main contents of his report translated by CnEVPost, which will be a must-read if you wish to understand NIO.
Frontrunner of the new car-making force
NIO is a leader in China’s new car-making force, founded in 2014 with global headquarters in Shanghai and China headquarters in Hefei, Anhui Province.
Its main business is the design, manufacture, and sales of smart connected electric vehicles, and it is a pioneer in the premium electric vehicle market in China.
Technology innovation, design-driven, and service-first are the three main characteristics of NIO.
NIO believes that smart, electric, and autonomous driving are the future of automobiles, so it is committed to continuously innovating industry-leading technologies and leading change.
NIO is committed to creating products that are pure, easy to use, and desirable, bringing a delightful experience to users.
NIO provides high-quality service that exceeds expectations, providing users with a pleasurable experience and increasing user satisfaction.
Key points in the history of NIO’s development:
- In 2014, NIO was founded.
- In 2015, NIO received Series A as well as Series B funding and won the Formula E championship.
- In 2016, NIO received Series C funding and EP9 was released.
- In 2017, NIO received Series C+ financing as well as Series D financing, and ES8 was launched.
- In 2018, NIO was listed on NYSE, and ES6 was launched.
- In 2019, ES6 started delivery and some ES8s were recalled.
- In 2020, NIO China headquarters was set in Hefei, EC6 was released and BaaS battery leasing service was started.
- In 2021, ET7 was unveiled and the battery swap station construction plan was released.
NIO is positioned as a luxury high-end pure electric vehicle, starting with SUV models and gradually enriching its product line.
NIO currently has three models on sale and one pre-sale model, with a price range of RMB 358,000 ($55,396)-624,000.
NIO ES8 is a mid-size SUV, ES6 and EC6 are mid-size SUVs, and the ET7 on pre-sale is a mid-to-large size sedan, which is expected to be delivered in the first quarter of 2022.

In 2022 NIO will launch Gemini, a new product also positioned at the high-end.
NIO ES8 monthly sales are stable, while ES6 and EC6 monthly sales are steadily increasing.
In June 2021, NIO delivered a record 8,083 vehicles, up 116.1 percent year-over-year. NIO delivered 95.9 percent of last year’s full-year volume in the first half of 2021.
The ET7, NIO’s first sedan, is now available for pre-order, and overall sales are expected to increase further as it gradually enriches its lineup.
NIO’s core team is experienced and involved in a wide range of fields, which has contributed to NIO’s development.
Its core management team members, William Li, Qin Lihong, Shen Feng, and Feng Wei have worked at BitAuto, Chery, Volvo China R&D, and CICC, respectively, in fields including the Internet, marketing, automotive R&D, and finance.
In August 2020, Reng Shaoqin, former Director of R&D at Momenta, a self-driving company, joined NIO as Assistant Vice President, responsible for the development of autonomous driving.
Since its inception, NIO has received support from top investors including JD Digits, Tencent Investment, Baidu Investment, Hillhouse Capital, and Sequoia China.
As of its IPO, NIO had raised over $2.2 billion in cumulative financing.
In April 2020, Hefei government-owned capital made a strategic investment of RMB 7 billion in NIO, and NIO China headquarters was located in the city.
On September 12, 2018, NIO landed on the New York Stock Exchange, raising about $1 billion and valuing about $6.4 billion, becoming the first stock of Chinese electric vehicles listed in the US.
In September 2020, NIO completed a private placement, raising $1.73 billion.
XPeng Motors has already listed on the Hong Kong stock exchange (HKEX) in July 2021, and NIO may likewise choose to list on HKEX.
NIO has established autonomous driving R&D centers, forward-looking concept R&D centers, styling centers, and a Norwegian branch in San Jose, Oxford, Munich, and Oslo, respectively.
NIO has already established an initial nationwide customer service system in the Chinese market and will officially announce its entry into the Norwegian market on May 6, 2021.
It will establish a direct sales and service network in Norway and will deliver the ES8, the first model to be sold overseas, in September.
NIO’s main models
The NIO ES8 was launched on December 16, 2017, and is positioned as a mid-size SUV with a price range of RMB 468,000 – 624,000 yuan.
As of June 2021, the total sales of ES8 were 41,633 units, with monthly sales basically stable at 1,400-1,600 units in the past year.
The ES8 is equipped with Mobileye Eye Q4 autonomous driving chip with FOTA support. It has 5 millimeter-wave radars and 12 ultrasonic sensors.
Its intelligent cockpit is equipped with NOMI artificial intelligence system with a round AMOLED screen.
The ES8 has a mobile Internet-based charging solution and an extensive network of charging facilities, and NIO has built a “rechargeable, replaceable and upgradeable” service system based on NIO Cloud technology.
NIO’s high-performance long-range mid-size SUV ES6 was launched on December 15, 2018, with a price range of RMB 358,000-526,000. As of June 2021, it has total sales of 58,794 units.
The ES6 features a high-strength aluminum plus carbon fiber composite architecture with a 0-100 km acceleration time of 4.7 seconds and a maximum combined range of 610 km.
It also supports upgrades to a 100-kWh battery system with individual customization and build-to-order models.
The NIO mid-size SUV EC6 was launched on July 24, 2020, with a price range of RMB 368,000 – 526,000 yuan. As of June 2021, it had total sales of 21,514 units.
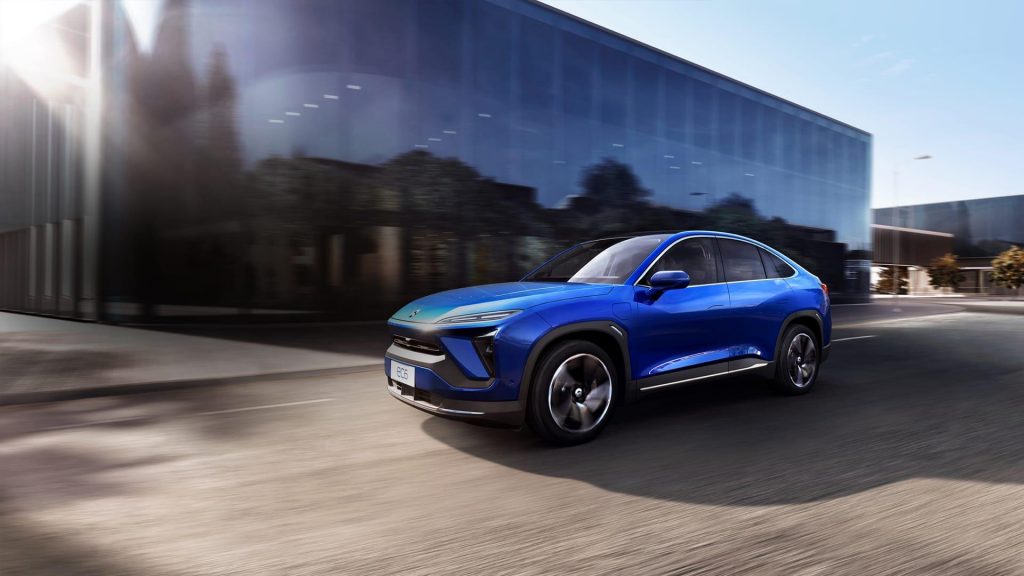

The EC6 has a coupe-like body with a low wind resistance coefficient of 0.26 Cd, 0-100 km acceleration time of 4.5 seconds and a combined range of 615 km.
The car supports an upgrade to a 100-kWh battery system and has an integrated dome-style glass roof.
The ET7 sedan, NIO’s first self-driving model, was launched on Jan. 9, 2021, with a price range of RMB 448,000 – 526,000, and has not yet been delivered.
The ET7 features the Aquila hyper-sensing system with 33 high-precision perception hardware, an 8-megapixel HD camera and ultra-long-range high-precision LiDAR.
Rapid revenue growth and loss reduction
NIO’s revenue has been growing rapidly since its launch along with the rising delivery volume.
In 2020, the company’s revenue was RMB 16.26 billion, up 107.77 percent year-over-year, and in the first quarter of 2021, revenue was RMB7.982 billion, up 481.82 percent year-over-year.
NIO has not yet achieved profitability, but the net loss has narrowed significantly.
NIO lost RMB 23.33 billion in 2018, RMB 11.41 billion in 2019 and RMB5.611 billion in 2020.
Thanks to the scale effect from production and sales volume growth, as well as cost reduction, NIO’s gross margin was -5.17 percent, -15.32 percent, 11.52 percent, and 19.48 percent from 2018 to the first quarter of 2021, respectively.
NIO’s net profit margin was -194.68 percent, -144.36 percent, -32.62 percent, and -5.65 percent for the first quarter of 2018 to 2021, respectively.
NIO’s R&D expenses from 2018 to 2020 were RMB 4 billion, RMB 4.43 billion, and RMB 2.49 billion, respectively.
From 2018 to 2020, NIO’s selling, administrative and general expenses were RMB 5.34 billion, RMB 5.45 billion, and RMB 3.93 billion, respectively.
NIO’s products are positioned in the luxury high-end market with emphasis on user experience, so it continues to invest in selling and administrative expenses.
With the rapid growth of revenue, its R&D, selling, and administrative expenses continue to decrease as a percentage of revenue.
Unlike the 4S store sales model of traditional car companies, NIO has adopted a direct sales model.
Thanks to the advantages of the sales model, the company’s inventory turnover days continued to decline from 2018 to the first quarter of 2021.
From 2019 to the first quarter of 2021, NIO’s accounts payable turnover days remain largely stable, while accounts receivable turnover days maintain a downward trend and operating capacity continues to improve.
Self-driving technology redefines driving experience
NIO’s on-sale models are now gradually equipped with L2 autonomous driving features, which assist drivers in driving operations while also bringing a different driving experience.
According to an IHS Markit survey, Chinese consumers are more receptive to new in-car technologies such as interconnectivity, OTA updates and autonomous driving than consumers in other major regions of the world. In-vehicle technology features have become an important factor in Chinese consumers’ vehicle purchase decisions.
Tesla sold 500,000 vehicles worldwide in 2020 and is expected to sell more than 800,000 vehicles worldwide in 2021.
None of the Chinese new car makers sold more than 50,000 units in 2020, and there is still much room for improvement.
NIO’s advantages
Electric motors, batteries and electronic controls are the core of the powertrain of new energy vehicles, and NIO’s XPT plant in Nanjing produces electric drive systems and battery systems for the company.
The XPT plant has a 240kW electric drive system workshop, a 160kW electric drive system workshop, an ESS energy storage system workshop and a complete vehicle pilot plant, with an annual production capacity of up to 300,000 sets.
In the material cost distribution of electric vehicles, battery, electric control and automotive electronics together account for about 65 percent of the total material cost of the vehicle, which is the main material cost.
NIO’s in-house developed and produced battery pack and electric drive systems help it to enhance its control of the supply chain, reduce costs and increase profitability.
NIO’s smart driving technology platform has been upgraded to NT2.0, with the capability of mass production of autonomous driving systems.
Based on the new platform, NIO has established a full-stack autonomous driving technology capability that includes perception algorithms, map positioning, control strategies and underlying systems.
The ET7, released on January 9, 2021, is equipped with NIO Autonomous Driving, a product based on the NT2.0 technology platform.
The new intelligent driving platform has greater potential for development and lays a solid foundation for NIO’s autonomous driving progression.
NIO’s NOMI is based on a powerful in-vehicle computing capability and cloud computing platform and integrates a voice interaction system and an intelligent emotion engine to create a new way of human-vehicle interaction.
It provides assistance in entering and exiting the vehicle, driving, navigating, and riding, transforming the car from a machine into a living, emotional partner.
With the addition of in-house developed technology, NIO can now update the entire vehicle’s five functional domains and 35 ECUs via OTA.
By October 2020, NIO had provided two years of OTA updates for vehicles, maintaining a monthly feature upgrade rhythm.
NIO has pushed a total of 39 major update packages to users, covering 4 models of the two generations of ES8, ES6, and EC6, adding 131 new features and completing 280 feature optimizations.
OTA technology is able to push newly developed features to owners, continuously optimize existing features and improve potential problems, allowing owners to enjoy the dividends of smart car technology development.
According to William Li, Chairman of NIO, the monthly production capacity of JAC’s NIO plant reached 7,500 units in January 2021.
Meanwhile, JAC has started to expand the plant. By the end of this year, JAC’s NIO plant will have an annual capacity of 150,000 units on a single shift and 300,000 units on a double shift.
In April 2021, the Neo Park in Hefei started construction, which is adjacent to Hefei Xinqiao Airport and covers an area of 16,950 mu, including an intelligent manufacturing area, an R&D living community and an ecological and cultural area.
The initial investment in Neo Park is RMB 50 billion yuan, and after completion, the annual output value will exceed RMB 500 billion yuan, the vehicle capacity will reach 1 million vehicles/year, and the battery capacity will reach 100GWh/year.
NIO’s NIO House is usually in the center of the business district of first-tier cities, with several functional areas including model display area, lecture area, library, co-working and parent-child area to provide value for users and enhance the height of the brand.

NIO Space, on the other hand, focuses on test drives and sales and is more cost-effective as construction, rent, and marketing expenses are significantly reduced compared to NIO House.
NIO House and NIO Space constitute a three-dimensional terminal marketing, experience, and sales network with clear positioning and hierarchy of NIO.
NIO Power is a mobile Internet-based power addition solution with a widely laid out charging facility network.
Relying on NIO Cloud technology, NIO has built an energy service system that is “rechargeable, replaceable and upgradeable”.
Users can install home charging piles or home fast charging piles at home, and use Supercharger, battery swap station, and charging car service outside.
NIO Service provides the first owner with three rights: free lifetime warranty, free lifetime roadside assistance and free lifetime connected car service, eliminating the user’s worries about using the car.
NIO Life brings good design and products into everyone’s daily life through more than 500 global designers, whose products cover clothes, food and daily necessities.
NIO Life enhances user experience through four major concepts: car, service, digital touchpoints and lifestyle beyond the car, forming a user community and building brand soft power.
This article was first published by Phate Zhang on CnEVPost, a website focusing on new energy vehicle news from China.
