In the trend for higher levels of autonomous driving, intelligent vehicles pose more stringent requirements in the aspects such as computing power, communication bandwidth, software, and security. This trend facilitates the evolution of automotive E/E architectures from domain centralized to multi-domain integrated, and then to the (quasi) central computing architecture. At present, there are primarily following five types of automotive multi-domain computing design ideas:
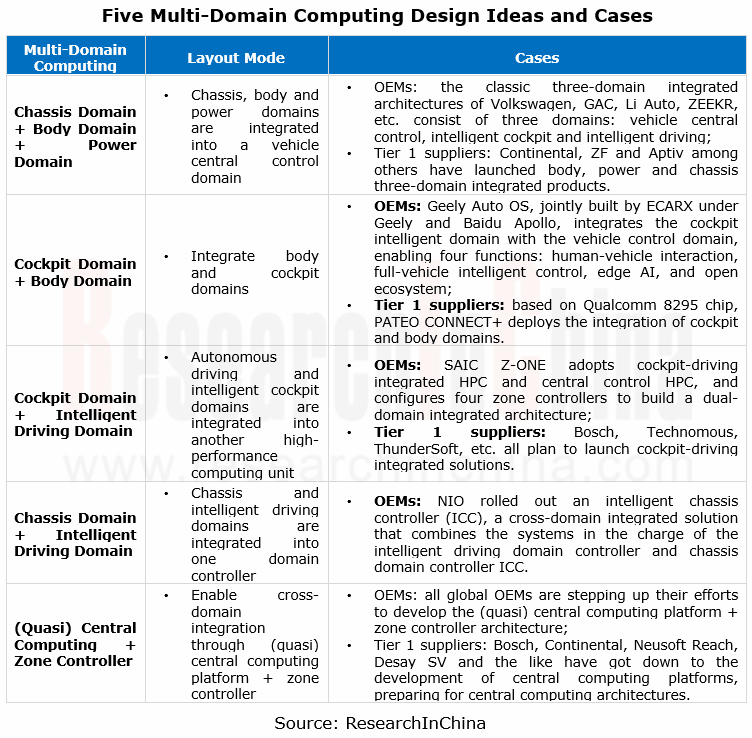
The driving and parking integration & the cockpit and driving integration are the important directions multi-domain computing heads in.
In terms of driving and parking integration, the low-speed parking function used to be integrated into cockpit domain to constitute a so-called cockpit-parking integrated solution. With the evolution to high computing power platforms, 2022 will be beyond doubt the first year of the development of L2+ driving and parking integration, and more vehicles will support multi-scenario autonomous driving, for example, turn signals for automatic lane change, ramp-to-ramp autonomous driving, home-AVP, and fully automated parking.
Cockpit-driving integration is the direction many OEMs and Tier 1 suppliers work towards. It is expected that mass production and installation of cockpit-driving integrated solutions will be achieved during 2024-2025. From chip vendors, it can be seen that Qualcomm 8795 chip that allows multi-domain integrated computing of cockpit and autonomous driving will be produced in quantities in 2024 at the earliest; Chinese suppliers like ThunderSoft and Haomo.AI have set about research and development; in addition to autonomous driving, NVIDIA Orin X will also fully integrate development of cockpit applications to enable fusion of autonomous driving and in-cabin algorithms through NVIDIA DRIVE IX software stack.
iMotion’s IDC high/low speed driving and parking integrated domain controller solution
iMotion concentrates on developing autonomous driving domain controllers. Following the acquisition of orders for more than 100,000 sets from ZEEKR 001 in October 2021, the company’s high computing power autonomous driving controllers have been designated by multiple first-tier OEMs like Great Wall Motor, Chery, Geely and SMART for a range of their vehicle models.
iMotion also launched a domain controller IDC product that integrates driving and parking capabilities like urban NOA and AVP. The IDC product has IDC MID (standard) and IDC HIGH (upgrade) versions, of which the standard version is to be delivered and mounted on new vehicle models of quite a few leading automakers in 2022.
iMotion’s end-to-end all-scenario intelligent driving solution takes the driving and parking integrated domain controller as the carrier. Based on L2++ intelligent driving and intelligent parking, this solution collects and trains unknown scene data and updates optimized algorithms by using hardware embedded points and remote software OTA update technology, and optimizing and verifying the big data closed-loop. It constantly improves intelligent driving algorithms in a bid to adapt to more complex scenarios, find application in ever more scenarios and eventually to be available to all scenarios.
In addition to driving and parking integration, the integration of intelligent driving and intelligent cockpit domains is also a megatrend. iMotion is working with its partners to explore multi-domain integrated solutions.
Neusoft Reach’s driving and parking integrated domain controllers keep upgrading and iterating.
Neusoft Reach’s fourth-generation autonomous driving domain controller X-Box is a new standard L2+ domain controller product developed according to SDV development model. Based on Horizon Journey 5 Series AI chips, the product offers L2+ driving and parking functions, and supports access of 8M cameras, 4D point cloud radars and LiDAR, with scenarios covering highways, urban expressways, some urban roads and multiple types of parking lots.
X-Box adopts SOA software architecture design scheme, that is, software and algorithms are developed using the modular and service-oriented development model. The product enables cooperative device-cloud autonomous driving under data closed-loop mechanism, and supports new-generation automotive E/E architectures. It enables intra-domain and cross-domain service subscription and discovery, flexible software deployment, and rapid iteration of application layer, and realizes such functions as fully open system architecture, open multi-dimensional full-stack software capability and joint development, allowing partners to quickly develop applications and reuse software. It also provides abundant software development tools for developer partners.
Meanwhile, in terms of safety and security X-Box is developed according to ISO 26262 functional safety and ISO 21434 cybersecurity standards. It implements the minimal risk strategy in typical driving and parking scenarios, and deploys secure boot/storage/upgrade/communication modules in connection systems at the vehicle, cloud and smartphone ends. It helps automakers to provide driving safety and cybersecurity guarantees for consumers. Neusoft Reach offers autonomous driving domain controller solutions for automakers at different tiers through standardized hardware, software platforms, and tool-based services.
SAIC Z-ONE’s cockpit-driving integrated HPC
SAIC Z-ONE plans to spawn a two-domain integrated E/E architecture in 2024, that consists of two high-performance computing units (HPC) and four zone controllers. Thereof, the cockpit-driving integrated HPC will be used to create the modular and scalable software and hardware integrated architecture that combines intelligent cockpit and high-level autonomous driving.
The vehicle central control domain has been the first to be mass-produced.
Some OEMs currently make crucial deployments in the integration of vehicle body, chassis and power domains into one central control domain that then combines with intelligent cockpit and intelligent driving domains to form a classic three-domain architecture. From time nodes, it can be seen that multiple vehicle models based on three-domain architectures were mass-produced and marketed during 2021-2022. The three-domain integrated architectures next will further introduce zone controllers for a smooth evolution to zonal architectures.
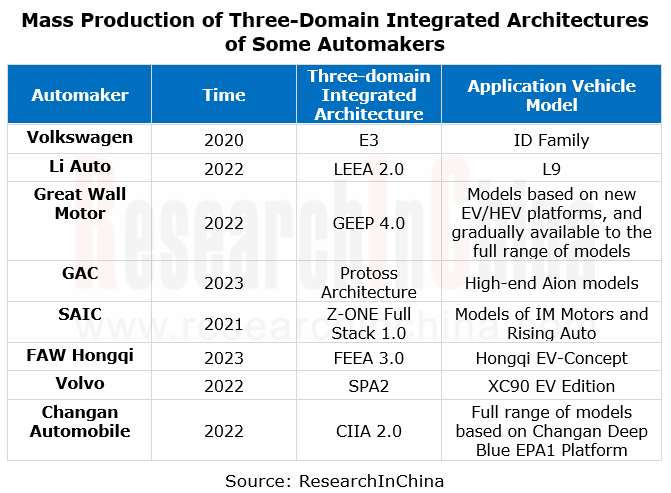
Li Auto’s three-domain integrated architecture: LEEA 2.0
In June 2022, Li Auto unveiled L9, its newest model that adopts three-domain integrated architecture. The whole car is divided into three domains: central control domain, autonomous driving domain and intelligent cockpit domain. The central control domain controller fuses with power, body and some chassis functions, enabling multi-domain integration.
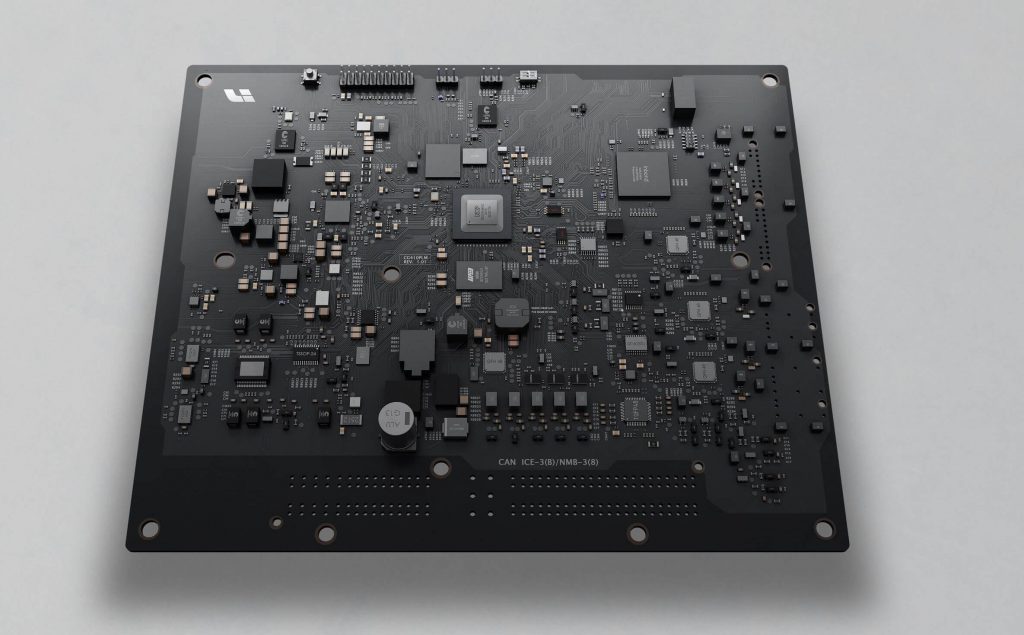
Aptiv’s Central Vehicle Controller (CVC)
At the CES 2022, Aptiv showed Central Vehicle Controller (CVC), its body, power and chassis three-domain integrated controller. The CVC can serve as a power and body controller, propulsion and chassis controller, data network router, gateway, firewall, zone master and data storage hub all rolled into one – or it can perform a mix of some of those functions. It is applicable to zonal architectures.
Zone controllers are the key component that carries “multi-domain + central computing”.
Zonal Control Unit (ZCU) is the central hub and the zonal data center for different types of sensor collector/actuator drivers in the physical zones of vehicles. It is an effective solution to carry physical interfaces of vehicles, distribute power and balance different input/output controls in the zones, thus supporting cross-domain integration inside smart cars.
The ZCU can cut ECU usage, lower wiring harnesses cost greatly, and reduce weight and communication interfaces, saving space and enabling higher utilization of computing power. At present, most OEMs have planned the use of 2 to 6 ZCUs in their next-generation multi-domain computing architectures.
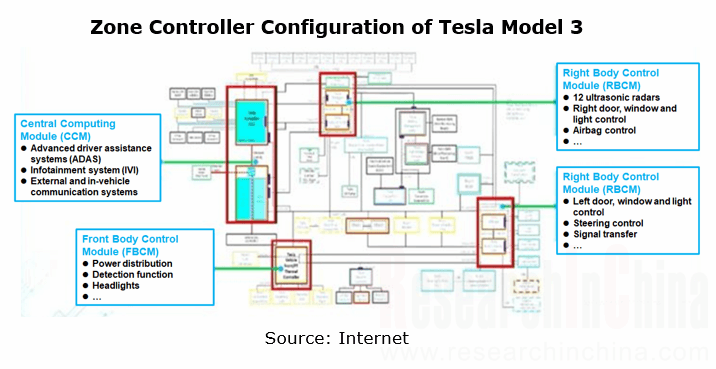
Tesla’s ZCU Configuration
In Tesla’s case, the central computing architecture of Model 3 uses three ZCUs respectively in the front body control module, the left body control module and the right body control module. They take on power distribution, drive and logic control in all physical zones. Tesla Model Y uses fewer ZCUs (2 units), cancels the front body control module, and integrates the function into the left and right body control modules, which means further integration of ZCU functions.
Aptiv’s ZCU Product – Power Data Center (PDC)
In January 2022, Aptiv introduced Power Data Center (PDC), its zone controller product that is installed on the front and rear sides of vehicle body.
Aptiv PDC abstracts the inputs/outputs (I/O) of sensors and actuators around the vehicle from the computing power (OSP, CVC, etc. responsible for processing), and also significantly simplifies hardware interchangeability by eliminating the device layer’s dependence on the computing layer via standardized service-based APIs.
