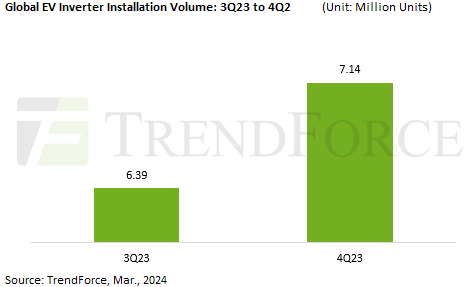
TrendForce’s latest market report on EV installers reveals that their global installation volume reached 7.14 million units in 4Q23—a roughly 12% increase from 6.39 million units in 3Q23. This growth is primarily due to the increase in EV sales in the last quarter compared to the third quarter. Among these, the inverter market’s main driving force comes from BEVs.
Inverters for BEVs accounted for approximately 53% of all EV inverter installations in 4Q23, covering a range of EVs including HEVs, BEVs, PHEVs, and FCVs. The EV inverter market itself expanded to an estimated $4.4 billion in 4Q23, with the BEV sector making the largest contribution at more than 60% of the market share.
A key factor in this growth is the technological advancement from traditional Si-IGBTs to SiC chips in inverter power components. This shift enhances the inverters’ voltage breakdown capability and conversion efficiency, improving vehicle range and enabling the introduction of high-voltage EV models for more efficient charging. In 4Q23, inverters installed in vehicles with voltages over 550V accounted for 9% of the total, a 1% increase from the previous quarter.
Further analysis by TrendForce shows that inverters equipped with SiC power chips made up 15% of the total inverter installations for the quarter. To meet the increasing demand for SiC chips, many automakers have established direct partnerships with upstream power semiconductor companies. A prime example is Li Auto’s strategic cooperation with UNT to develop products in SiC chip design and research.
Automakers and Tier 1 suppliers are introducing x-in-1 electric drive systems to improve vehicle range and reduce weight, with inverters playing a pivotal role. China leads in this area of technological integration, with companies like BYD, Leapmotor, and Seres launching 8-in-1 electric drive systems, and Dongfeng Motor unveiling a groundbreaking 10-in-1 system. Meanwhile, global Tier 1 suppliers like BOSCH, Denso, and ZF continue to focus on developing 3-in-1 systems.
(Note: X-in-1 electric drive systems—developed to boost the overall range of NEVs—center around the electric motor and inverter. It integrates essential components such as onboard chargers (OBC), DC/DC converters, and battery management systems (BMS) into one system. This not only reduces the need for high-voltage cables but also decreases vehicle weight and enhances driving range.)

